Industrial automation applications are at the forefront of technological advancements, transforming industries by unlocking efficiency, fostering innovation, and driving growth. From manufacturing to supply chain management, automation has revolutionized the way businesses operate. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the world of industrial automation applications, their types, key uses, and their impact on modern businesses.

What Are Industrial Automation Applications?
Understanding the Basics of Industrial Automation
Industrial automation refers to the use of technology to control and monitor industrial processes with minimal human intervention. Automation systems include robots, sensors, software, and control systems that enhance productivity, accuracy, and efficiency.
Why Industrial Automation Applications Are Essential for Modern Businesses
Modern businesses face the challenge of staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market. Industrial automation applications enable companies to:
- Streamline operations.
- Reduce errors and downtime.
- Enhance product quality.
- Optimize resource utilization.
By leveraging automation, businesses can achieve higher efficiency while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
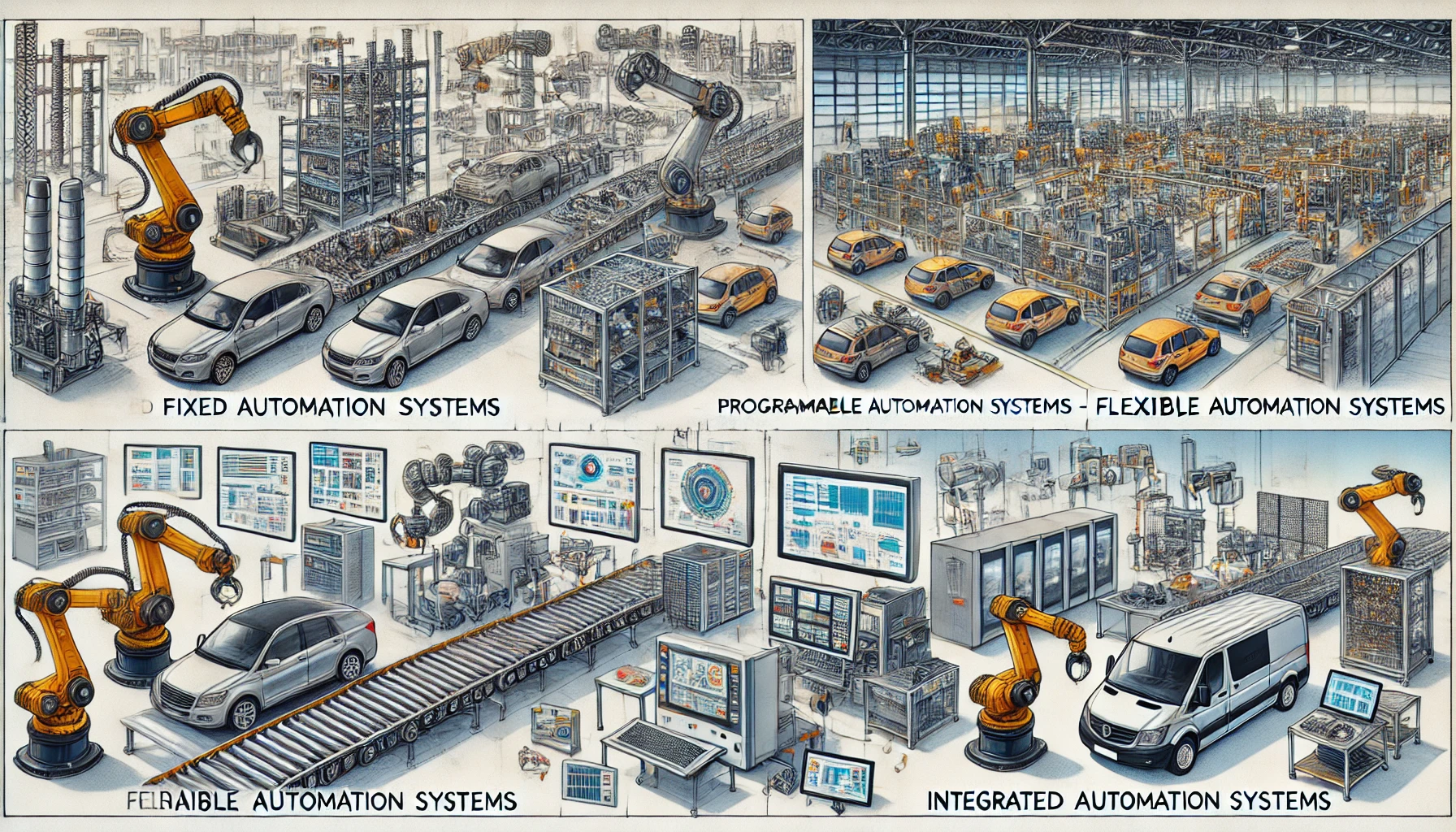
Types of Industrial Automation Systems
Fixed Automation Systems
Fixed automation systems are designed for high-volume production processes where the equipment performs a specific set of tasks repeatedly.
Common Examples of Fixed Industrial Automation Applications
- Assembly lines in automotive manufacturing.
- Conveyor systems in packaging industries.
- Injection molding machines in plastic production.
Programmable Automation Systems
These systems allow reprogramming to adapt to different tasks, making them ideal for batch production.
Industrial Automation Applications Using Programmable Systems
- CNC machines for custom product designs.
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for warehouse operations.
- Robotics used in food processing industries.
Flexible Automation Systems
Flexible systems provide real-time adaptability to production needs, supporting low-to-medium volume manufacturing.
The Role of Flexible Automation in Business Growth
Flexible automation enables businesses to:
- Quickly adjust to market demands.
- Produce diverse product ranges.
- Minimize downtime during transitions.
Integrated Automation Systems
Integrated systems combine hardware and software for end-to-end automation, enabling seamless control of industrial processes.
How Integrated Systems Optimize Industrial Processes
- Monitoring and controlling entire production lines.
- Integrating enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
- Enhancing data-driven decision-making.

Key Industrial Automation Applications in Business
Applications in Manufacturing and Production
Manufacturing industries are among the largest adopters of industrial automation applications.
Improving Quality Control with Automation
- Automated inspection systems for defect detection.
- Precision welding and cutting tools for accuracy.
- Machine vision systems for quality assurance.
Logistics and Supply Chain Optimization
Automation in logistics improves efficiency and reduces costs throughout the supply chain.
Reducing Costs with Industrial Automation Applications
- Automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) for inventory management.
- Drone technology for faster delivery solutions.
- Predictive analytics for demand forecasting.
Energy Management Systems
Industrial automation plays a critical role in achieving energy efficiency and sustainability.
Boosting Sustainability Through Automation
- Smart grids for real-time energy optimization.
- IoT sensors for tracking energy consumption.
- Automated controls for reducing wastage.
The Role of an Industrial Automation Application Engineer
Key Responsibilities of Automation Engineers
Automation engineers are vital to designing, implementing, and maintaining automation systems. Their responsibilities include:
- Developing customized automation solutions.
- Testing and debugging automation software.
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Skills Required for Industrial Automation Projects
- Proficiency in programming languages like PLC and SCADA.
- Knowledge of robotics and control systems.
- Problem-solving and analytical skills.
Contribution to Industry-Specific Solutions
Automation engineers design solutions tailored to specific industries, enhancing their operational efficiency.
Examples of Real-World Industrial Automation Applications
- Automated bottling plants in the beverage industry.
- Smart factories in electronics manufacturing.
- Automated traffic control systems in urban infrastructure.

Benefits of Industrial Automation Applications
Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency
Industrial automation applications significantly enhance productivity by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks. Automated systems ensure consistent performance and eliminate human errors, allowing businesses to achieve greater output with less effort.
Streamlining Business Operations
Automation streamlines operations by integrating systems and processes across departments. For instance, automated supply chain management systems help monitor inventory, manage logistics, and ensure timely delivery, reducing downtime and increasing overall efficiency.
Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
Industrial automation applications play a crucial role in reducing costs while optimizing resources. Automated systems use energy more efficiently and reduce waste, contributing to sustainable practices.
Minimizing Errors with Automation Systems
By replacing manual processes with precise automated solutions, businesses can minimize errors that lead to costly rework. Quality control systems powered by automation ensure products meet high standards, improving customer satisfaction and reducing expenses.
Challenges and Solutions in Industrial Automation
Addressing Cybersecurity Risks in Automation
As industries adopt automation, cybersecurity has become a critical concern. Automated systems often connect to the internet, making them vulnerable to cyber threats. Ensuring the security of industrial automation applications is essential for safeguarding sensitive data and operations.
Implementing Secure Industrial Automation Applications
To mitigate cybersecurity risks, companies must implement robust security measures such as encryption, firewalls, and regular system updates. Partnering with cybersecurity experts and conducting routine audits can further enhance the security of automated systems.
Training and Skill Development Needs
The integration of advanced technologies in automation demands a skilled workforce capable of managing and maintaining these systems. Without proper training, businesses may face challenges in maximizing the potential of their industrial automation applications.
Preparing Engineers for Advanced Automation Roles
Investing in training programs and workshops helps engineers acquire the skills needed to operate and troubleshoot complex automation systems. Collaborative efforts with educational institutions can bridge the skill gap, ensuring a steady supply of qualified professionals.
Future Trends in Industrial Automation Applications
AI and Machine Learning in Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing industrial automation by enabling systems to learn, adapt, and make decisions in real time. These technologies enhance efficiency and open doors to innovative applications.
Examples of AI-Driven Automation Systems
AI-driven robotic arms used in manufacturing can adjust their movements based on real-time data, improving precision and reducing waste. Similarly, predictive maintenance systems analyze equipment performance to foresee and prevent potential failures.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) and Smart Factories
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) integrates connected devices and sensors, creating smart factories where data-driven insights drive decision-making. IIoT enhances industrial automation applications by enabling real-time monitoring and control.
How IIoT Enhances Industrial Automation Applications
IIoT applications include condition monitoring systems that detect anomalies in equipment and send alerts before failures occur. These systems improve operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and increase profitability.
FAQ Section
What are the main types of industrial automation systems?
Industrial automation systems are classified into fixed automation, programmable automation, and flexible automation. Fixed automation is used for high-volume production with limited flexibility. Programmable automation allows for reconfiguration for batch production. Flexible automation adapts to product changes in real-time, offering versatility for dynamic operations. Each type serves unique operational needs, ensuring efficiency and precision in manufacturing processes.
How do industrial automation applications improve business efficiency?
Industrial automation applications boost business efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, reducing manual intervention, and enhancing accuracy. They streamline workflows, minimize errors, and optimize resource utilization, resulting in increased productivity. Additionally, automation reduces labor costs and operational downtime, enabling businesses to achieve faster production cycles and improved overall performance, creating a competitive edge in their respective industries.
What are some examples of industrial automation applications in manufacturing?
Examples of industrial automation in manufacturing include robotic assembly lines, which increase production speed and precision. Automated quality control systems inspect products for defects in real-time, ensuring consistency. Predictive maintenance solutions use data analytics to identify potential equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and repair costs. These applications enhance overall productivity and product quality in modern manufacturing processes.
What are the benefits of implementing industrial automation systems?
Implementing industrial automation systems offers several benefits, including improved operational efficiency through streamlined processes. Cost reduction is achieved by minimizing labor expenses and waste. Enhanced workplace safety is ensured by automating hazardous tasks. Automation also delivers higher product quality by reducing human error and maintaining consistency. These advantages make automation a valuable investment for businesses seeking long-term success and competitiveness.
How does AI enhance industrial automation applications?
AI enhances industrial automation by enabling systems to learn, adapt, and optimize processes. It facilitates predictive maintenance by analyzing equipment data to foresee potential issues. AI-powered systems make smarter decisions, improving accuracy and precision in tasks. Furthermore, AI-driven automation allows for real-time adjustments to changing conditions, ensuring efficiency and agility in dynamic industrial environments, paving the way for smarter manufacturing solutions.
What are the future trends in industrial automation applications?
Future trends in industrial automation include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) for smarter decision-making and predictive maintenance. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) connects devices for real-time data sharing and analytics. Smart factories leverage advanced automation technologies for optimized production. Sustainable automation focuses on energy-efficient solutions and reducing environmental impact, shaping a future of innovation and eco-conscious manufacturing.
Conclusion
Industrial automation applications are a cornerstone of modern industrial practices, driving efficiency, innovation, and growth across sectors. By adopting the right automation systems, businesses can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and remain competitive in today’s dynamic market. Whether it’s in manufacturing, logistics, or energy management, the potential of industrial automation applications is immense and continues to grow. For businesses aiming to unlock their full potential, embracing industrial automation is no longer an option but a necessity.




