Deep learning (DL) is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables machines to learn and make decisions independently. Unlike traditional programming, which requires human intervention to define rules, DL allows AI systems to automatically improve their performance as they process more data. It’s based on Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) that try to replicate how the human brain works, allowing machines to learn from vast amounts of unstructured data.
The Growth and Relevance of Deep Learning

Over the past decade, deep learning has emerged as a game-changer in AI. Once considered a niche area, it has now become essential in fields like Natural Language Processing (NLP), image recognition, and predictive analytics. Key milestones, such as the development of neural networks capable of identifying objects in images and powering voice assistants, demonstrate how DL has evolved. Its growth is fueled by improvements in computational power, access to big data, and more sophisticated algorithms.
Purpose of the Article
In this article, we’ll dive into how deep learning is reshaping AI and what that means for our future. From enhancing decision-making abilities to transforming industries like healthcare and finance, it is making its mark everywhere. Let’s explore its vast potential and the role it will play in the coming years.
The Core Concepts of Deep Learning
A. Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
At the heart of deep learning are artificial neural networks (ANNs). These networks consist of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that mimic the structure and function of the human brain. Each node processes input data, passing it through several layers to extract meaningful patterns. The depth and complexity of these networks allow AI models to handle more intricate tasks compared to traditional machine learning models.
B. Training and Learning Process
Deep learning models learn by analyzing massive datasets and adjusting the weights of the connections between neurons. The training process involves feeding data through the network and comparing the predicted output with the actual result. The model adjusts itself iteratively to reduce the error, becoming more accurate over time. This process requires powerful hardware, such as GPUs, and vast amounts of labeled data to achieve meaningful results.
C. Types of Deep Learning Models
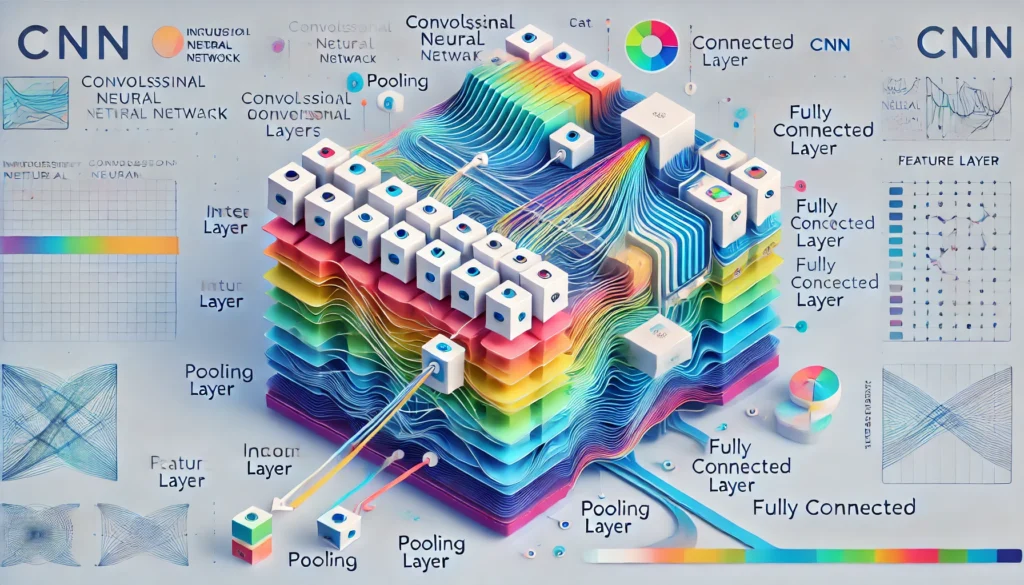
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Primarily used for image-related tasks like object recognition and facial recognition. CNNs are designed to identify spatial hierarchies in images.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Best suited for sequential data, such as text or speech. RNNs can remember previous inputs in a sequence, making them ideal for tasks like language translation.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): These are used to generate new data, such as images or music, by pitting two networks against each other in a creative process.
III. How Deep Learning is Changing AI
A. Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency
One of the key advantages of DL is its ability to improve the accuracy and efficiency of AI models. With deep learning, AI systems can now process vast amounts of data and make decisions faster and with higher precision. For example, DL algorithms power modern image recognition systems, enabling facial recognition technology and automated tagging on social media platforms.
B. Automating Complex Tasks
It is revolutionizing industries by automating tasks that were once complex and labor-intensive. In healthcare, DL algorithms can analyze medical images, diagnose conditions like cancer, and recommend personalized treatment plans. In industries like finance, deep learning models are being used for fraud detection and to make investment predictions.
C. Breaking Barriers in Natural Language Processing (NLP)
It has propelled the field of natural language processing (NLP), allowing AI systems to understand and generate human language in ways previously unimaginable. Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa use deep learning to interpret voice commands. Furthermore, it is used in language translation tools, chatbots, and sentiment analysis, making communication between humans and machines more intuitive.
IV. Real-World Applications of Deep Learning
A. Healthcare and Medicine
In healthcare, deep learning has become indispensable. It helps in diagnosing diseases, predicting health outcomes, and even developing new drugs. Deep learning models analyze medical images, like MRIs and X-rays, to detect abnormalities such as tumors or fractures with remarkable accuracy. Additionally, it assists in personalized medicine by analyzing genetic information to suggest the best treatments for individual patients.
B. Autonomous Vehicles
Deep learning is the driving force behind self-driving cars. By processing data from cameras, LiDAR, and radar, AI models help autonomous vehicles understand their surroundings, recognize pedestrians, and navigate complex environments. This technology is paving the way for safer, more efficient transportation systems.
C. Finance and Banking
In the world of finance, AI is transforming how banks assess creditworthiness, detect fraudulent activities, and personalize services. Algorithms analyze transaction histories and other data points to predict future behaviors, allowing banks to offer tailored financial advice and prevent fraud.
D. Entertainment and Media
From Netflix recommendations to AI-generated music, advanced AI technologies are shaping the entertainment industry. It’s used to personalize content based on user preferences and even create entirely new forms of entertainment, like AI-created art and music.
E. Environmental and Sustainability
Advanced AI technologies also have the potential to address global challenges like climate change. It can predict environmental patterns, optimize energy consumption, and improve disaster response efforts, contributing to sustainability initiatives worldwide.
V. The Future of Deep Learning and AI
A. Advancements on the Horizon
The future of deep learning is exciting, with upcoming technologies like explainable AI, which aims to make DL models more transparent and understandable to humans. Additionally, quantum computing holds the potential to supercharge AI models, enabling them to process even larger datasets faster than ever before.
B. Ethical Concerns and Challenges
As DL continues to evolve, it brings with it ethical concerns. Issues like bias in AI models, data privacy, and the potential for AI misuse need to be addressed. Researchers and governments must collaborate to establish regulations and guidelines to ensure deep learning is used responsibly.
C. How Deep Learning Will Shape the Workforce
It is not just transforming technology but also the job market. While automation may replace some jobs, it will also create new roles requiring specialized skills. The need for AI and deep learning experts will grow, and professionals will need to upskill to remain competitive in this evolving landscape.
VI. Conclusion
Deep learning is an incredibly powerful technology that is fundamentally changing AI and how we interact with machines. From enhancing accuracy in decision-making to revolutionizing industries like healthcare and finance, its impact is undeniable. As we move forward, It will continue to play a major role in shaping our future.
The future of DL holds tremendous promise. As it continues to advance, it will unlock new possibilities across industries, improve our lives, and bring about groundbreaking innovations. However, as we embrace these changes, we must also remain mindful of the ethical considerations that come with such transformative technologies.
FAQs
1. What makes deep learning different from traditional machine learning?
- Deep learning (DL) is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with many layers to analyze complex data. Traditional machine learning often requires manual feature extraction, while DL automatically extracts features from raw data.
2. How does deep learning improve AI decision-making?
- Deep learning enhances AI by enabling models to process and learn from vast amounts of unstructured data. This results in more accurate predictions and faster decision-making, especially in tasks like image recognition and speech processing.
3. What industries are benefiting from deep learning?
- Industries like healthcare, finance, autonomous vehicles, entertainment, and environmental sustainability are already leveraging deep learning to optimize processes, improve efficiency, and create new solutions.
4. What are the ethical concerns surrounding deep learning?
- Ethical concerns include data privacy, bias in AI models, and the potential for deep learning systems to be used maliciously. Addressing these concerns requires clear regulations and a focus on fairness and transparency.
5. What is the future of deep learning?
- The future of deep learning includes advancements like explainable AI and quantum computing, as well as wider adoption across various industries. It will continue to shape our world and bring about significant technological changes.


