The world of autonomous vehicles (AVs) is rapidly evolving, and with it, the regulations governing their development, testing, and deployment. As we enter 2025, strict autonomous vehicle regulations are key to making sure these advanced technologies are safe, ethical, and dependable for everyone. In this article, we’ll know the current regulatory landscape, the challenges faced by stakeholders, and strategies to navigate these regulations.
What Are Autonomous Vehicles (AVs)?
Autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving cars, are vehicles capable of sensing their environment and operating without human intervention. AVs use a combination of sensors, cameras, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning algorithms to navigate and perform tasks like braking, accelerating, and steering.
Types of Autonomous Vehicles
- Level 1-2 (Assisted Driving): These vehicles require human intervention but feature assistance like adaptive cruise control.
- Level 3-4 (Conditional and High Automation): These vehicles can handle most driving tasks but may still require a human to intervene in certain conditions.
- Level 5 (Full Automation): Vehicles that require no human input, capable of fully autonomous driving in all environments.
Brief History of Autonomous Vehicles
The concept of autonomous vehicles dates back to the 1920s, but it wasn’t until the 2000s that significant breakthroughs in AI and sensor technology made AVs a reality. With companies like Waymo and Tesla leading the way, the regulatory environment has been playing catch-up to ensure safe and effective deployment.
Why Are Strict Autonomous Vehicle Regulations Necessary?
Strict autonomous vehicle regulations are critical for several reasons:
- Safety: To ensure that AVs can operate safely on public roads, avoiding accidents, and protecting passengers and pedestrians.
- Public Trust: Regulations help establish consumer confidence, ensuring the technology is safe and reliable.
- Ethical Considerations: AVs must make life-or-death decisions in some situations (e.g., unavoidable accidents), requiring ethical guidelines.
- Data Protection: AVs collect vast amounts of personal and driving data, making privacy laws essential.
While regulations are vital, they also present challenges, especially in balancing innovation with safety and public trust.
The Current Landscape of Autonomous Vehicle Regulations
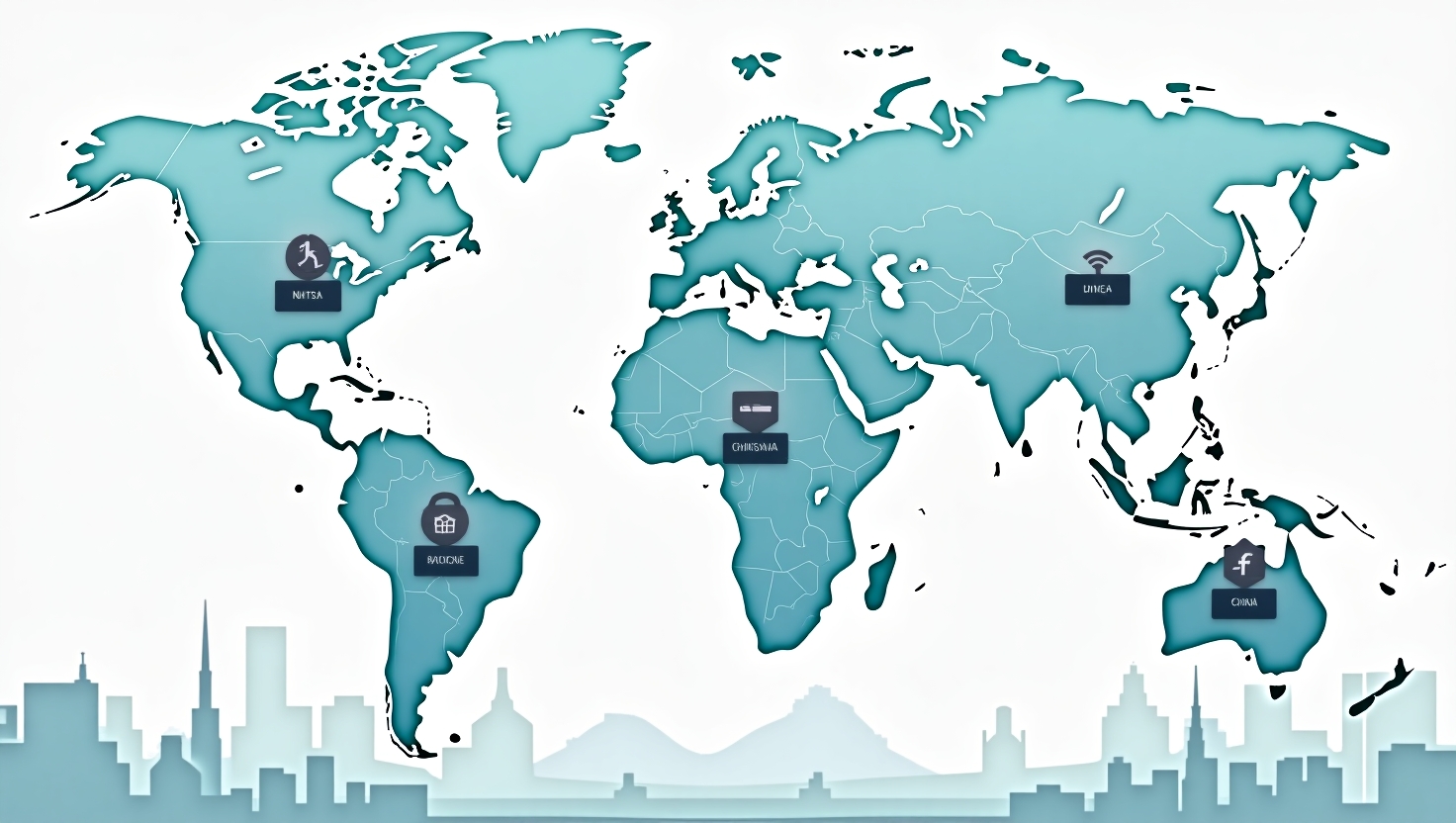
Global Regulatory Differences
Autonomous vehicle regulations vary significantly across the globe. In the United States, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) sets safety standards, but states like California have more specific rules for AV testing. Meanwhile, Europe has the European Union’s regulations that focus on cybersecurity and data protection for AVs. In contrast, China is pushing aggressively for AV development with less stringent rules initially.
Regulatory Bodies Involved
Several key organizations oversee autonomous vehicle regulations:
- NHTSA (USA): Sets national safety standards for AVs.
- UNECE (Europe): Works toward global vehicle safety standards, including AV guidelines.
- SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers): Provides classifications of vehicle automation levels, from Level 1 to Level 5.
Evolution of Regulations (2020-2025)
Over the past five years, strict autonomous vehicle regulations have become more comprehensive, focusing on aspects like cybersecurity, data privacy, and safety protocols. However, many areas still lack clear guidelines, particularly around liability and insurance.
Key Areas of Strict AV Regulations in 2025
A. Safety Standards
Safety is the cornerstone of strict autonomous vehicle regulations. AVs must adhere to rigorous standards for:
- Crash Avoidance Systems: AVs must be equipped with advanced sensors to detect and avoid obstacles, ensuring passenger safety.
- Emergency Braking: Mandatory systems that allow AVs to stop automatically in emergency situations.
B. Ethical and Liability Issues
Who is liable if an autonomous vehicle causes an accident? This is a critical concern. Governments are working to define liability laws for AVs, balancing the interests of manufacturers, drivers, and passengers.
C. Data Privacy and Cybersecurity
With AVs collecting vast amounts of data, including GPS, speed, and personal information, robust data privacy and cybersecurity measures are required to protect users from hacking or unauthorized data access.
D. Environmental Regulations
As AVs become more common, regulators are considering their environmental impact. Regulations focus on reducing emissions from production processes and ensuring energy-efficient operations, especially with electric-powered autonomous fleets.
E. Insurance and Certification
Insurance companies are adjusting their policies to cover autonomous vehicles, while AV manufacturers must adhere to strict certification processes to prove their vehicles meet safety and legal requirements before they hit the market.
Challenges Faced by Stakeholders

A. Manufacturers and Developers
For AV manufacturers, complying with strict autonomous vehicle regulations involves significant costs, lengthy approval processes, and delays in testing. The regulatory uncertainty also hampers innovation and market entry for smaller companies.
B. Governments and Regulatory Bodies
Governments are under pressure to regulate effectively without stifling innovation. Striking the right balance between fostering technological advancement and ensuring safety remains a key challenge.
C. Consumers and Public Acceptance
Public trust in AVs is crucial for widespread adoption. The fear of accidents or the unknown aspects of AVs often lead to skepticism. Public education and transparent regulation can help build confidence.
D. Legal and Insurance Industries
The legal and insurance industries face evolving frameworks. Legal systems must address new liability concerns, and insurers are working to create new models for AV policies that account for the unique risks posed by these vehicles.
VI. Strategies for Navigating Strict AV Regulations
A. Collaboration Between Stakeholders
Public-private partnerships are essential for developing clear, fair, and effective regulations. Collaboration between governments, tech companies, and the insurance sector can foster innovation while ensuring safety.
B. Technological Innovations to Meet Regulations
Advancements in AI, machine learning, and sensor technology will help AVs comply with safety standards. Continuous improvements in these areas ensure that AVs remain compliant with evolving regulations.
C. Lobbying and Advocacy for Balanced Regulations
Manufacturers and developers are actively lobbying for clearer regulations that promote innovation without compromising safety. Engaging with policymakers helps shape a more balanced regulatory environment.
D. Training and Certification Programs
To meet the growing demand for AVs, there is a need for specialized training programs for AV-related roles, ensuring that workers are prepared for the industry’s regulatory challenges.
Future of Autonomous Vehicle Regulations Beyond 2025

A. Potential Regulatory Changes
As AV technology continues to advance, strict autonomous vehicle regulations will evolve. Expect to see more refined standards, particularly regarding the ethical decision-making capabilities of AVs, as well as clearer liability laws.
B. Global Standardization
The global AV market would benefit from standardized regulations. Collaboration between countries to create universal guidelines could accelerate the development and deployment of AVs worldwide.
C. Impact of Technological Advancements
The rapid growth of AI, machine learning, and smart infrastructure will likely influence future autonomous vehicle regulations. The development of smart cities and connected roads will drive changes in regulatory frameworks to accommodate these new technologies.
Conclusion
In 2025, strict autonomous vehicle regulations are shaping the AV industry, ensuring safety, ethical decision-making, and legal clarity. While navigating these complex regulations presents challenges, collaboration between stakeholders, technological innovation, and effective advocacy can help pave the way for a successful autonomous future. The road ahead may be full of hurdles, but with the right approach, the journey toward a fully autonomous transportation system can be achieved.
FAQs
Q1: Why are autonomous vehicles regulated so strictly?
- Strict regulations ensure the safety of both passengers and pedestrians, maintain public trust, and prevent data privacy violations.
Q2: How are AV regulations different in various countries?
- Different countries have distinct regulations. For instance, the U.S. focuses on safety and testing, while Europe emphasizes cybersecurity and data protection.
Q3: Will the regulations for AVs become stricter over time?
- Yes, as technology evolves, regulations are likely to become more refined to address new challenges related to safety, ethics, and liability.
Q4: How do manufacturers cope with strict regulations for AVs?
- Manufacturers need to invest heavily in compliance efforts, including testing, certification, and adapting to various national regulations.
Q5: What role does AI play in meeting AV regulations?
- AI helps AVs meet safety standards by improving decision-making capabilities, crash avoidance, and route optimization, all while ensuring compliance with regulatory guidelines.



