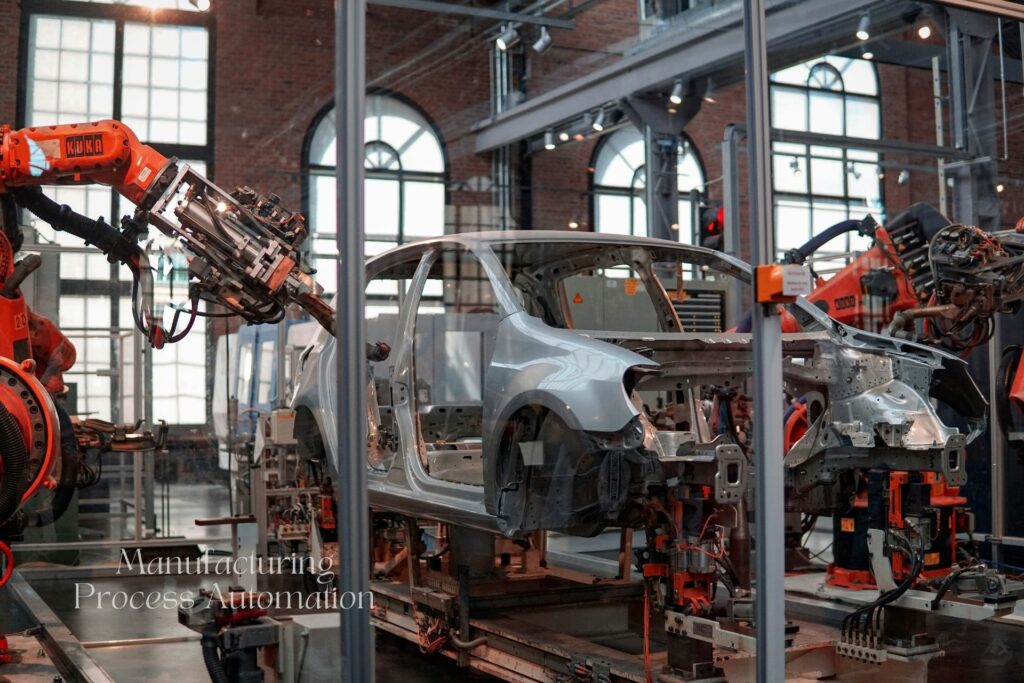
Manufacturing process automation has become essential for efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness in the modern manufacturing landscape. By leveraging advanced technologies, automated systems streamline various processes within the manufacturing environment, resulting in better outcomes, reduced costs, and improved product quality. This article will explore how manufacturing process automation transforms industries, its benefits, and why more businesses are embracing this approach to enhance their operations.
What is Manufacturing Process Automation?

Manufacturing process automation uses control systems such as computers, robots, and other automated equipment to control industrial processes and machinery. This system replaces manual labor with automated machinery and processes that can operate continuously with minimal human intervention. Automation technology is pivotal in modern manufacturing practices, from assembly lines to quality control.
By incorporating these automated systems, manufacturers can ensure faster production, higher precision, and increased workplace safety. Automating tasks such as assembly, welding, painting, and packaging helps companies meet higher demand while maintaining consistent product quality.
How Does Manufacturing Process Automation Work?
Manufacturing process automation works through machines, control systems, and real-time data analysis. Here’s a breakdown of how it operates:
1. Machine Automation

Machine automation involves using robots and automated machines to perform repetitive tasks like assembly, welding, or painting. These machines are designed to work with high precision and speed, significantly improving production efficiency. They are often used in tasks that require heavy lifting, fine detail, or repetitive motion, which could lead to errors if performed manually.
2. Control Systems and Software
Control systems are the brains behind the automation process. These systems use software to monitor and control equipment, machinery, and processes. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems are vital in controlling and optimizing production steps.
Manufacturers can integrate different process components with advanced software, from inventory management to scheduling, creating a smooth and coordinated workflow. The software also ensures that machinery operates efficiently, preventing breakdowns and minimizing downtime.
3. Real-Time Data Monitoring
The use of real-time data is a key feature of manufacturing process automation. Through sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) devices, data can be collected on every part of the production cycle. This allows manufacturers to monitor temperature, pressure, and production speed, ensuring processes remain within optimal parameters.
By collecting and analyzing this data, businesses can proactively detect equipment failure or inefficiency, allowing them to make timely adjustments and avoid costly downtime.
The Benefits of Manufacturing Process Automation
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity

One of the most significant advantages of manufacturing process automation is the increase in efficiency. Automated systems can work around the clock without breaks or fatigue, drastically improving production speeds. Automated systems can perform tasks faster and more consistently than human workers, allowing manufacturers to produce more products in less time.
Additionally, automated systems reduce the need for human intervention in repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more complex responsibilities and innovation.
2. Improved Product Quality
Automation ensures every product is produced to the exact specifications without human error. Machines and robots can perform tasks with precision, reducing the chances of defects or variations in quality. This level of consistency ensures that the product quality remains high, regardless of the production volume.
Furthermore, automated systems can monitor production processes in real-time, detecting issues and making adjustments instantly to maintain the desired product standards.
3. Cost Reduction
Although the initial investment in manufacturing process automation can be substantial, the long-term savings are undeniable. Automation reduces labor costs, decreases the likelihood of costly errors, and minimizes downtime by ensuring equipment operates efficiently. Automated systems can also reduce waste by optimizing material usage and reducing overproduction.
Over time, businesses experience a return on investment (ROI) through reduced operating costs, making automation a financially viable solution for many industries.
4. Enhanced Worker Safety
Heavy machinery or hazardous materials can pose a risk to workers in many manufacturing environments. Manufacturing process automation helps mitigate these risks by allowing machines to perform dangerous tasks, such as handling toxic substances or working with high-temperature equipment.
Automation significantly improves workplace safety by reducing the need for humans to operate in potentially harmful environments. It reduces the risk of accidents and injuries.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Manufacturing process automation provides businesses with greater flexibility and scalability. Automated systems can be easily adjusted or reprogrammed to handle different products or production volumes. As businesses grow, automation systems can be expanded to accommodate increased demand or new product lines without requiring a complete infrastructure overhaul.
Common Applications of Manufacturing Process Automation
Manufacturing process automation can be applied to various industries and processes. Below are some of the most common applications:
1. Assembly Line Automation
Automated assembly lines use robots and automated machines to perform tasks such as picking, placing, and assembling components. This application is widely used in the automotive industry, where precise and consistent assembly is required to meet safety standards.
2. Packaging Automation
Packaging automation systems handle product packaging, including filling, sealing, labeling, and palletizing. These systems speed up packaging while maintaining quality control and reducing waste. This application is common in the food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods industries.
3. Quality Control Automation
Automated quality control systems use sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence (AI) to inspect products for defects or deviations from quality standards. This ensures that only products that meet the required specifications are shipped to customers, improving product consistency and reducing returns.
4. Material Handling Automation
Material handling automation involves moving materials around the production floor using conveyors, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and robotic arms. This reduces the need for manual labor, speeds up material transport, and minimizes workplace injury risk.
Challenges of Manufacturing Process Automation
While there are numerous advantages to manufacturing process automation, there are also some challenges to consider:
1. High Initial Investment
The cost of implementing automated systems can be significant, especially for small to medium-sized businesses. However, many companies find that the long-term cost savings, increased productivity, and improved quality outweigh the initial investment.
2. Technical Expertise
Automated systems require skilled personnel to manage, maintain, and troubleshoot. Businesses may need to invest in training their workforce or hire new talent with the necessary technical expertise.
3. System Integration
Integrating automation technology into existing manufacturing processes can be complex. Companies must ensure that the new systems are compatible with their current infrastructure and that the integration process is smooth to avoid disruptions in production.
Conclusion
Manufacturing process automation is no longer a luxury but a necessity in today’s competitive business world. By adopting automated systems, companies can increase efficiency, reduce costs, improve product quality, and create safer working environments. Whether it’s assembly, packaging, quality control, or material handling, automation is crucial in optimizing operations.
As the technology continues to evolve, businesses that embrace manufacturing process automation will be better positioned to adapt to changing market demands and stay ahead of the competition. By investing in automation, manufacturers can unlock new levels of productivity and profitability, securing long-term success in the industry.
FAQs About Manufacturing Process Automation
1. How can manufacturing process automation improve efficiency?
Manufacturing process automation improves efficiency by replacing manual labor with automated systems that can operate continuously, perform tasks faster, and reduce errors. Automated systems ensure that processes are streamlined, consistent, and accurate, leading to faster production cycles.
2. What industries benefit most from manufacturing process automation?
Manufacturing process automation benefits many industries, including automotive, electronics, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. It can benefit any industry that requires high production volumes, precision, and quality control.
3. Is manufacturing process automation suitable for small businesses?
Yes, automation of the manufacturing process can benefit small businesses. While the initial investment may be higher, automation can lead to long-term cost savings, increased productivity, and higher product quality. Small businesses can start by automating specific processes and scale as their operations grow.



