In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the demand for more efficient, precise, and scalable manufacturing processes is at an all-time high. This is where automation machine design comes into play. By integrating advanced technology into the design of machinery and systems, automation machine design revolutionizes production lines, making them more productive, reliable, and adaptable. This article will explore what automation machine design is, why it is essential, how it works, its basic theory, as well as its advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, we will look at the functions, impacts, and applications of automatic machine design in various industries.
What Is Automation Machine Design?

Automation machine design refers to the process of designing machinery and systems that can operate with minimal human intervention, often through the use of robotics, sensors, and computer controls. This design focuses on creating automated systems that can perform repetitive or complex tasks with high precision and efficiency, improving productivity while reducing errors and operational costs.
Automation machine design is typically used in manufacturing, logistics, and various other industries where high-volume production is essential. Through the implementation of automated machinery, manufacturers can increase production speeds, improve product quality, and lower the cost of labor.
Why Is Automation Machine Design Important?

The role of automation machine design is indispensable in modern industries. Here’s why:
-
Increased Productivity: Automated systems can operate around the clock without the need for rest, significantly boosting production rates and throughput.
-
Consistency and Precision: Automation ensures that every task is performed with the same high level of accuracy, which is essential for products that require tight tolerances or uniformity.
-
Cost Savings: While the initial investment in automated machines may be high, the long-term savings are significant. Reduced labor costs, fewer errors, and less waste contribute to lower operational costs.
-
Workplace Safety: By automating dangerous tasks, workers are removed from hazardous environments, reducing the likelihood of injuries and improving overall safety.
-
Scalability: Automation machine design makes it easier for manufacturers to scale up production when demand increases, allowing them to respond quickly to market changes.
How Does Automation Machine Design Work?
Automation machine design involves the integration of various technologies and components that enable machines to operate independently. Here’s how it works:
-
Sensors and Actuators: Sensors are used to monitor the machine’s environment, detecting variables like temperature, pressure, and position. Actuators, on the other hand, convert electrical signals into physical actions, enabling the machine to move parts or perform tasks.
-
Control Systems: A central computer or controller interprets sensor data and issues commands to the machine’s actuators. These control systems are often programmable, allowing for custom workflows based on specific requirements.
-
Robotics: Many automation systems incorporate robots to perform tasks that require dexterity, precision, or repetitive motion. Robots can be programmed to handle a wide range of functions, from assembly to packaging.
-
Software: Automation machine design often relies on sophisticated software to control the entire system. This software can optimize processes, perform diagnostics, and enable remote monitoring and control.
-
Integration: One of the key aspects of automation machine design is the seamless integration of these components. The various elements work together in harmony to perform tasks efficiently, ensuring that all processes run smoothly without human intervention.
Basic Theory Behind Automation Machine Design
At its core, automation machine design is based on the principles of control theory, robotics, and systems engineering. The basic theory centers on the use of feedback loops to control the system’s behavior. Feedback loops allow the machine to adjust its actions based on real-time input from sensors.
Control theory governs how systems maintain their performance over time, adjusting parameters like speed, position, and force. Robotics provides the tools to automate physical tasks, while systems engineering ensures that all components of the machine function together effectively. By applying these principles, automatic machine designers create machines that are efficient, reliable, and capable of performing complex tasks autonomously.
Advantages of Automation Machine Design
The benefits of automation machine design are numerous and impactful:
-
Higher Efficiency: Automated machines can run continuously, leading to higher throughput and fewer delays in the production process.
-
Improved Product Quality: With automation, the chances of human error are greatly reduced, leading to more consistent, high-quality products.
-
Labor Cost Reduction: Automation reduces the need for manual labor, which can lower overall operational costs and improve profitability.
-
Flexibility: Automated systems can be reprogrammed or reconfigured for different tasks, making them highly adaptable to changing production needs.
-
Enhanced Data Collection: Automation systems often collect valuable data during production, which can be analyzed to improve processes, reduce waste, and predict maintenance needs.
Disadvantages of Automation Machine Design
While the benefits are substantial, automation machine design also has its limitations:
-
High Initial Cost: The upfront investment required for automation equipment can be significant, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises.
-
Complexity in Setup: Setting up automated systems often requires specialized knowledge and technical expertise, which can pose challenges during installation and configuration.
-
Job Displacement: As more tasks become automated, there is a concern about job loss for workers who may be displaced by machines.
-
Maintenance Requirements: While automation can reduce labor costs, it often requires specialized maintenance and troubleshooting, which can lead to additional costs.
-
Limited Creativity: Machines excel at repetitive tasks but may struggle with complex problem-solving or creative tasks that require human intuition.
Functions of Automation Machine Design

The automation machine design process involves several key functions, each crucial to the success of the system:
-
Assembly: Automated systems can handle the assembly of components, from basic tasks like screwing parts together to more complex processes such as welding or bonding.
-
Inspection: Automated machines can perform high-precision inspections, identifying defects or deviations in products with high accuracy.
-
Material Handling: Automated systems can move materials across production lines, reducing the need for human labor in this often repetitive task.
-
Packaging: From sorting to sealing, automated machines can handle all aspects of packaging, ensuring products are packaged efficiently and consistently.
-
Quality Control: Automation systems can be equipped with vision systems and sensors to continuously monitor product quality and make adjustments in real-time.
Impacts of Automation Machine Design
The impacts of automation machine design are far-reaching, particularly in industrial sectors:
-
Increased Global Competitiveness: Automation allows companies to reduce costs, improve product quality, and speed up production, helping them remain competitive in a global market.
-
Innovation in Manufacturing: By automating labor-intensive processes, manufacturers have the freedom to explore innovative designs, production techniques, and customizations.
-
Sustainability: Automation systems can improve resource management, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste, contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
-
Economic Growth: By improving efficiency and creating high-quality products, automation supports economic growth by driving down costs and opening up new markets.
Applications of Automation Machine Design
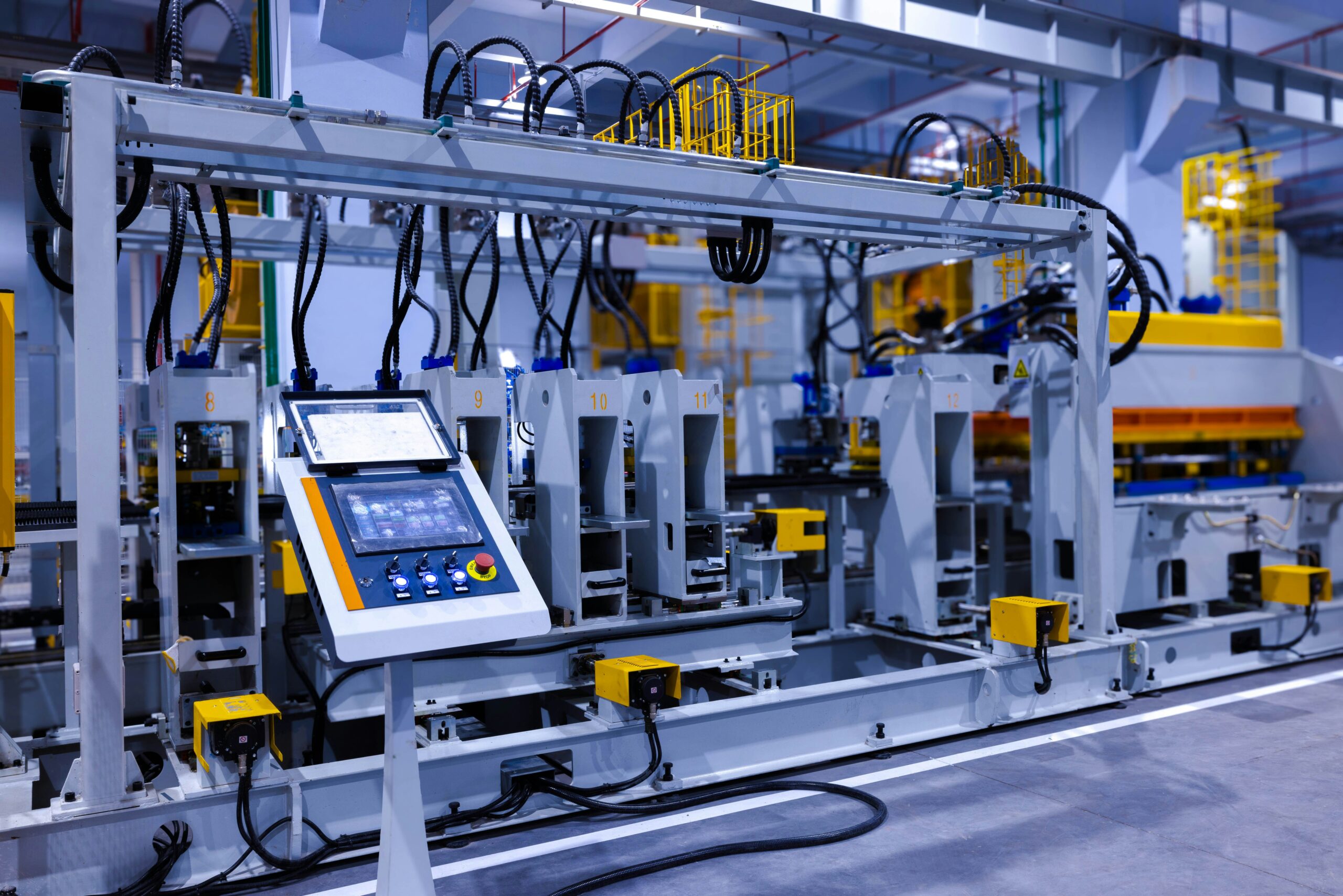

Automation machine design is used across various industries to streamline operations and improve efficiency. Some key applications include:
-
Automotive Industry: Automation systems are used in car assembly lines, performing tasks like welding, painting, and assembling parts with precision.
-
Electronics Manufacturing: Automated systems handle the assembly of electronic components, ensuring high accuracy and minimizing defects.
-
Pharmaceutical Industry: Automation machines are used for packaging, labeling, and quality control in drug manufacturing, ensuring compliance with stringent regulations.
-
Food and Beverage: Automation systems help in processing, packaging, and sorting food products, meeting high demand while maintaining hygiene and quality standards.
-
Aerospace: Automation machine design is used for tasks like precision assembly and inspection of complex components in aircraft manufacturing.
Conclusion: The Future of Automation Machine Design
The potential of automation machine design is vast, and as technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of automated systems. From reducing production costs to increasing product consistency and quality, automation is becoming a vital part of modern manufacturing. Though there are challenges to address, such as high initial costs and job displacement concerns, the advantages far outweigh the drawbacks. As we move forward, automation will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of industries worldwide.
FAQs
1. What is automation machine design?
Automation machine design refers to creating machines and systems that perform tasks automatically with minimal human intervention. It uses robotics, sensors, and computer controls to improve efficiency, consistency, and productivity in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
2. What are the benefits of automation machine design?
The key benefits of automation machine design include increased productivity, improved product quality, cost savings, enhanced workplace safety, and scalability. Automated systems can operate continuously, ensuring precision and reducing the chances of human error, leading to more efficient operations.
3. How does automation machine design work?
Automation machine design works by integrating sensors, actuators, robotics, and control systems. Sensors monitor conditions like pressure and position, while actuators carry out physical tasks. A central computer processes data and commands, optimizing machine performance and reducing the need for human intervention.
4. What industries benefit from automation machine design?
Automation machine design benefits industries such as automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and aerospace. By automating repetitive tasks, these industries can improve production speed, consistency, and quality, ensuring better resource management and reducing operational costs.
5. What are the challenges of automation machine design?
Challenges include high initial costs, the need for specialized knowledge, and potential job displacement due to automation. Additionally, automated systems require regular maintenance and may have limitations in handling complex or creative tasks, requiring continuous adaptation and investment.




I have recently started a blog, the info you offer on this site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
That means a lot—thank you for your kind words! I’m so glad the content has been helpful for your new blog journey. Wishing you all the success, and feel free to stop by anytime to share your progress or ask questions!
fantastic points altogether, you just gained a new reader. What would you recommend about your post that you made some days ago? Any positive?
Thank you for the kind words, and welcome! We’re glad you enjoyed the content. As for the post from a few days ago, it expands on similar ideas with practical examples and actionable insights, which many readers have found helpful. We’d love to hear your thoughts once you’ve had a chance to read it.
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I think that you should write more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
I completely agree—sometimes the most important conversations are the ones people are most hesitant to have. I’m glad you found the discussion valuable, and I definitely plan on exploring this further. Thanks for the encouragement!
Magnificent web site. A lot of useful info here. I’m sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And obviously, thanks in your effort!
Thank you very much for your kind words and for sharing the site with others. We’re glad you found the information useful, and we truly appreciate your support and encouragement!
I got what you mean , regards for putting up.Woh I am glad to find this website through google.
Thank you for your feedback! We’re glad the content was clear and helpful. It’s great to hear you found us through Google—welcome, and we hope you continue to enjoy the site!
Interesting blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog shine. Please let me know where you got your design. With thanks
Thank you for your kind words! Our theme is custom-made to fit our content and style, which allows for flexibility and uniqueness. If you’d like, we can share tips on how to customize a theme to make your blog stand out as well. We appreciate your interest and support!
You really make it appear so easy together with your presentation but I find this topic to be really one thing that I believe I would by no means understand. It seems too complicated and extremely wide for me. I am having a look forward on your subsequent put up, I will try to get the hang of it!
Thank you for your honest feedback! I try to break things down as simply as possible, and I’m glad you’re giving it a try. More beginner-friendly posts are coming—stay tuned!
Very interesting points you have remarked, thanks for putting up.
Thank you! I’m glad you found the points interesting and appreciate your support.
Admiring the time and energy you put into your website and in depth information you present. It’s nice to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same outdated rehashed material. Wonderful read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
Thank you so much! I really appreciate the kind words and the support. I’m glad you found the content fresh and valuable—more updates coming soon!
Almost all of what you mention happens to be supprisingly appropriate and it makes me wonder the reason why I hadn’t looked at this with this light previously. Your piece really did turn the light on for me personally as far as this particular subject goes. Nevertheless at this time there is actually one point I am not necessarily too comfy with and whilst I make an effort to reconcile that with the actual core idea of the position, permit me observe exactly what the rest of the subscribers have to point out.Nicely done.
Thank you for your detailed feedback! I’m glad the post offered a new perspective for you. It’s great that you’re thinking critically about the topic, and I look forward to hearing what other readers have to say as well.
You are my breathing in, I possess few web logs and occasionally run out from to post : (.
That truly means a lot to me—thank you! I’m really glad the content inspires you. We all hit creative blocks sometimes, so don’t worry. Keep going, and feel free to drop by anytime for fresh ideas.
You are my inspiration , I possess few web logs and sometimes run out from to post .
Thank you so much! I’m glad I could be an inspiration. Hang in there—you’ll find plenty of ideas to keep your blogs going!